Optimization of Phosphatidylcholine and Tween 80 Composition in the Formulation of Icariin Transfersome as a Transdermal Delivery System using Design-Expert
Downloads
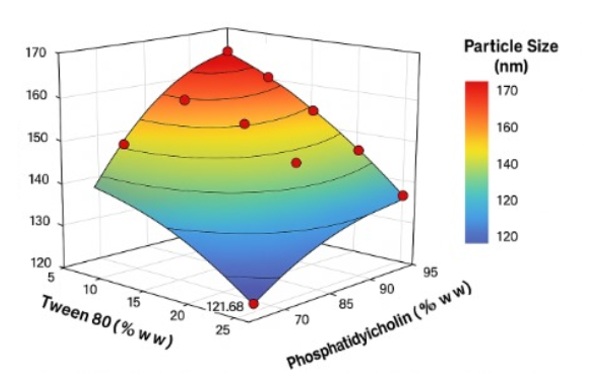
Icariin is the main flavonoid of Epimedium sp. and has phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitor (PDE5I) activity; however, its low water solubility and membrane permeability limit its oral bioavailability. The transferosome-based transdermal drug delivery system approach is considered promising because it can increase skin penetration and avoid the first-pass metabolism. This study aims to optimize the composition of phosphatidylcholine and Tween 80 in icariin-loaded transfersome vesicles to produce optimal physicochemical characteristics for transdermal applications. Method: Icariin transfersome was formulated using a thin-film hydration method with variations in phosphatidylcholine and Tween 80 concentrations. Optimization is performed using the Simplex Lattice Design (SLD) in Design Expert 13 software. The observed responses included particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, and Entrapment efficiency (EE%). The results of this study are the optimal formula of icariin transfersome, with a ratio of phosphatidylcholine and Tween 80 of 95%: 5%, resulting in ideal vesicle characteristics, namely a particle size of 106.15 nm, a zeta potential of -22.67 mV, a Polydispersity Index (PDI) of 0.37, and an Entrapment efficiency of 86.96%.
Downloads
Liu QW, Yang ZH, Jiang J, Jiang R. Icariin modulates eNOS activity via effect on post-translational protein-protein interactions to improve erectile function of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Andrology. 2021 Jan 1;9(1):342–51. doi: 10.1111/andr.12875
Indratmoko S, Nurani LH, Wahyuningsih I. Enhancement of lcariin aphrodisiac effect by self nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) method Journal of Advanced Pharmacy Education and Research. 2024 Jan 24;14(1):34–9. doi: 10.51847/8pmv24zvhv
Tang C, Meng K, Chen X, Yao H, Kong J, Li F, et al. Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of amorphous icaritin nanoparticles prepared by a reactive precipitation technique. Molecules. 2021 May 2;26(10). doi: 10.3390/molecules26102913
Andini S, Jufri M, Djajadisastra J. Formulasi dan Uji Penetrasi Sediaan Gel Transfersom yang Mengandung Kojyl 3 Amino Propil Fosfat sebagai Pencerah Kulit. Jurnal Kefarmasian Indonesia 2016 August;6(2). doi: 10.22435/jki.v6i2.2948.
Surini S, Nastiti PD, Putri AR, Putri KSS. Formulation of andrographolide transfersomes gel for transdermal delivery: A preliminary study. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. 2020 Mar 1;12(Special Issue 1):187–91. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2020.v12s1.FF043
Amnuaikit T, Limsuwan T, Khongkow P, Boonme P. Vesicular carriers containing phenylethyl resorcinol for topical delivery system; liposomes, transfersomes and invasomes. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2018 Sep 1;13(5):472–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2018.02.004
Putri SO, Iswandi I, Kuncahyo I. Optimization and Formulation of Fenofibrate Transfersome Using The Thin Layer Hydration Method. Riset Informasi Kesehatan. 2023 Dec 29;12(2):277. doi: 10.30644/rik.v12i2.773
Wulansari E, Siswanto A. Article history: Combination of HPMC and PVA using Factorial Design Method. Jurnal Kefarmasian Indonesia. 2025;15(1):34–45. doi: 10.22435/jki.v15i1.6700
Liu J, Cheng Q, Wu X, Zhu H, Deng X, Wang M, et al. Icariin Treatment Rescues Diabetes Induced Bone Loss via Scavenging ROS and Activating Primary Cilia/Gli2/Osteocalcin Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2022;11(24). doi: 10.3390/cells11244091
Zhao R, Zhou Y, Shi H, Ye W, Lyu Y, Wen Z, et al. Effect of Gestational Diabetes on Postpartum Depression-like Behavior in Rats and Its Mechanism. Nutrients. 2022 Mar 1;14(6). doi: 10.3390/nu14061229
El Zaafarany GM, Awad GAS, Holayel SM, Mortada ND. Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int J Pharm. 2010 Sep;397(1–2):164–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.06.034
Gupta R, Singhal M, Nimisha N. Transferosomes as an Efficient Carrier System for better Therapeutic response of Targeted Drug Delivery System. Res J Pharm Technol. 2022 Feb 26;913–20. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00153
Amalia TR, Maulidya V, Sastyarina Y. Karakterisasi dan Pengaruh Komposisi Kitosan terhadap Stabilitas Ukuran Nanopartikel Ekstrak Bawang Dayak (Eleutherine americana Merr.) menggunakan Metode Gelasi Ionik. Jurnal Mandala Pharmacon Indonesia. 2024 Jun 30;10(1):68–73. doi: 10.35311/jmpi.v10i1.487
Danaei M, Dehghankhold M, Ataei S, Hasanzadeh Davarani F, Javanmard R, Dokhani A, et al. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Vol. 10, Pharmaceutics. MDPI AG; 2018. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10020057
Takechi-Haraya Y, Ohgita T, Demizu Y, Saito H, Izutsu K ichi, Sakai-Kato K. Current Status and Challenges of Analytical Methods for Evaluation of Size and Surface Modification of Nanoparticle-Based Drug Formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Jul 20;23(5):150. Doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02303-y
Dalimunthe GI, Syahputra RA. Edge Activator: Effect of Concentration Variation of Tween 80 on Characteristics and Rate of Difusion transfersome sodium diclofenac. Journal Syifa Sciences and Clinical Research. 2021;3(2). doi: 10.37311/jsscr.v3i2.11914
Ode Sitti Zubaydah W, Nur Janna Kurniawati dan. Optimasi Fosfatidilkolin dan Span 80 sebagai Penyusun Vesikel Transfersom Natrium Diklofenak menggunakan Design-Expert. Vol. 2022, J.Food Pharm.Sci. 2022. doi: 10.22146/jfps.5581
Wang J, Zhu G, Wang X, Cai J, Xie L, Zheng W, et al. An injectable liposome for sustained release of icariin to the treatment of acute blunt muscle injury. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2020 Sep 1;72(9):1152–64. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13314
Duangjit S, Opanasopit P, Rojanarata T, Ngawhirunpat T. Evaluation of Meloxicam-Loaded Cationic Transfersomes as Transdermal Drug Delivery Carriers. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013 Mar 14;14(1):133–40. doi: 10.1208/s12249-012-9904-2
Leonyza A, Surini S. Optimization of sodium deoxycholate-based transfersomes for percutaneous delivery of peptides and proteins. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics. 2019 Sep 1;11(5):329–32. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2019v11i5.33615.
Copyright (c) 2025 Jurnal Kefarmasian Indonesia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.















